Central Banks: policy and effects
Information is not investment advice
Central bank is the key element of a country’s financial system. It controls the money supply, interest rates, and the national currency. In addition, a central bank usually supervises the commercial banking system of its country.
Central banks have many important functions. The main one is to maintain price stability by controlling inflation. A central bank is supposed to promote the economic health of a country.
Central banks have an impact on the market. A central bank’s intervention is one of the well-known expressions. A bank enters the foreign exchange market to buy or sell currency in order to influence exchange rates. Another way to intervene is to throw necessary information into the market. It is called a verbal intervention.
To get a good grasp of any central bank’s policy, you need to know its main objectives, basic tasks, schedule and agenda of its meetings. In addition, you need to be able to predict the possible impact of its undertakings on the future value of the affected currency.
FED
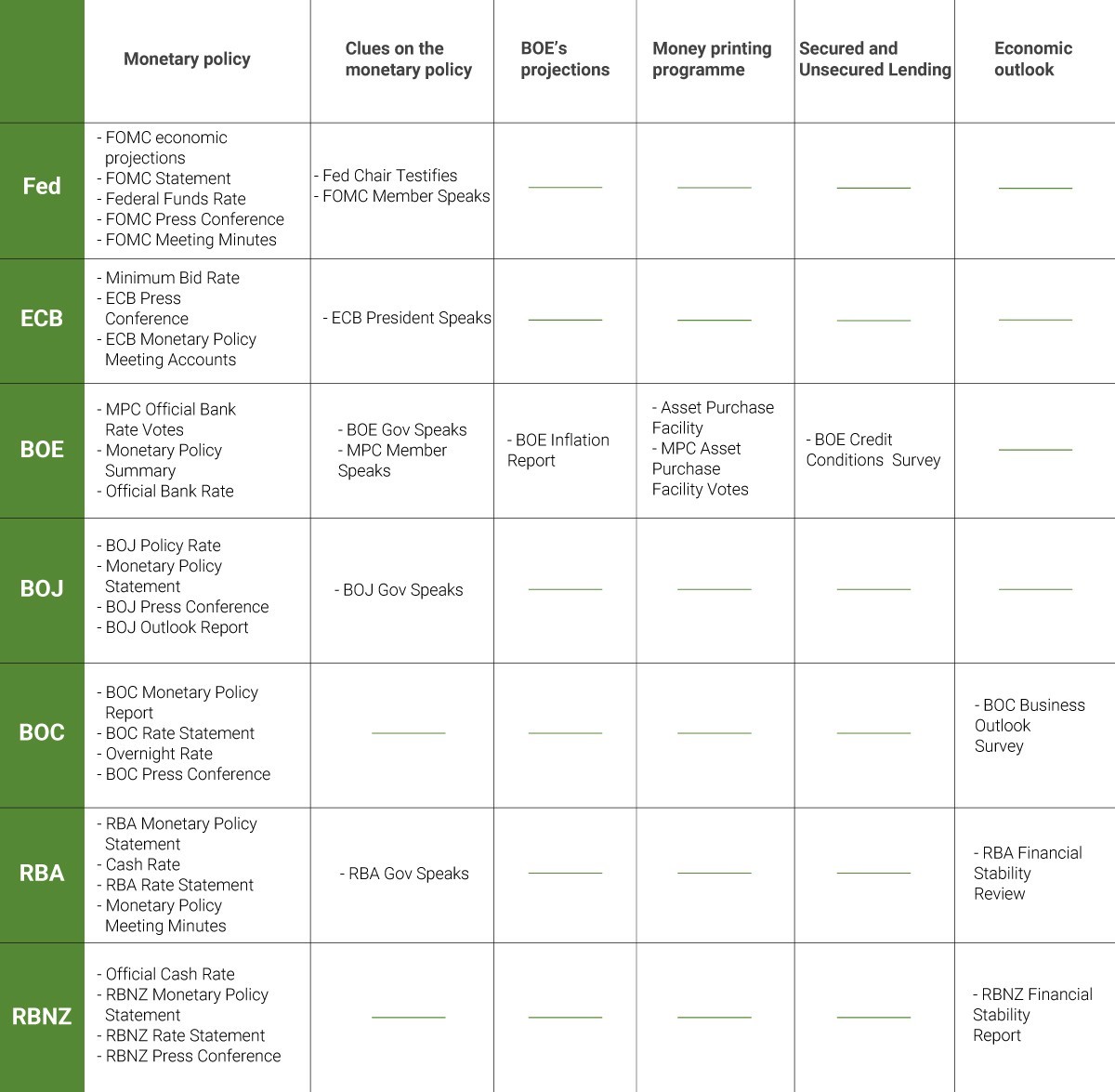
The Federal Reserve (Fed) is the central bank of the United States. The Fed includes 12 regional Federal Reserve Banks located in big cities throughout the country. They gather economic information in order to enable the Fed to choose the adequate monetary stance. Monetary policy decisions at the Fed are made by the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) which consists of 7 members of the Board of Governor and 5 Reserve Bank presidents.
The FOMC meetings represent one of the most highly-anticipated events and have a great impact on the Forex market. The Fed announces an interest rate (federal funds rate), provides the economic outlook that influenced its rate decision and offers some clues on future statement changes.
Meetings that are followed by press conferences (usually in March, June, September, and December) are the most important as rate changes happen at them.
In addition, note that 3 weeks after every meeting the central bank releases its minutes. This document contains information on the previous decision and may contain the Fed’s intentions about its future monetary policy.
While making its policy decisions, the Federal Reserve takes into account such economic indicators as GDP growth, core CPI, core PCE price index, average hourly earnings, nonfarm payrolls.
Traders try to predict actions of the Fed and their expectations make the US dollar rise and fall.
ECB
The European Central Bank (ECB) is the central bank of the 19 countries of the European Union that adopted the common currency – the euro – in 2002.
Its main tasks are to define and implement monetary policy for the euro area; take charge of the national banks of the eurozone members; conduct foreign exchange operations; promote smooth operating of payments systems and take care of the euro area’s foreign currency reserves.
The ECB makes monetary policy decisions every 6 weeks. These decisions are followed by press conferences and have a big impact on the dynamics of the euro. The minutes of the ECB meetings don’t usually affect the market much.
BoE
The Bank of England (BoE) is the central bank of the United Kingdom that traces its history since 1694. The main tasks of the BoE do not differ from the tasks of other central banks. The central bank supports the economic growth of the UK, maintains inflation and sets interest rates.
The Bank’s monetary policy committee (MPC) meets once a month in order to set monetary policy. The central bank releases the meeting minutes right after the meeting. In addition, meetings are often followed by press conferences of BoE Governor.
Once a quarter the BoE releases its Inflation report that contains its projections for GDP and inflation.
Moreover, the central bank publishes information on the money printing program (total value of money the BOE will create and use to purchase assets in the open market).
BOJ
The main objective of the Bank of Japan (BOJ) is pretty much the same as that of the other regulators: “to carry out currency and monetary control to achieve the price stability”.
BOC
The Bank of Canada (BOC) exists “to regulate credit and currency in the best interests of the economic life of the nation.” One of the features of the BOC’s work is its business outlook survey. About 100 businesses with the most significant shares in GDP rate business conditions. This survey gives good clues on the monetary policy.
RBA
The main aim of the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) is to “contribute to the stability of the currency, full employment, and the economic prosperity and welfare of the Australian people”. The central bank serves to the Government and its agencies, and to overseas central banks and official institutions. Furthermore, it maintains Australia’s gold and foreign exchange reserves.
RBNZ
The Reserve Bank of New Zealand (RBNZ) “manages monetary policy to maintain price stability, promotes the maintenance of a sound and efficient financial system, and supplies New Zealand banknotes and coins.”
Note: it is worth to say that speeches of central banks’ members influence the economy too as there are no people who are more tied to the monetary policy. Words of the central banks’ heads affect markets the most.
What to follow on the economic calendar:
Other articles in this section
- Timeframes
- Renko charts Japanese candlestick chart
- Types of charts
- Heiken Ashi
- Pivot Points
- ZigZag
- Moving Average
- Williams’ Percent Range (%R)
- Relative Vigor Index (RVI indicator)
- Momentum
- Force index
- Envelopes
- Average True Range
- CCI (Commodity Channel Index)
- Parabolic SAR
- Stochastic Oscillator
- Relative Strength Index
- Oscillators
- ADX indicator
- Bollinger bands
- Trend indicators
- Introduction to technical indicators
- Trend
- Technical analysis
- Fundamental factors
- Fundamental analysis
- Fundamental vs technical analysis