Bill Williams est le créateur de certains des indicateurs de marché les plus populaires : Awesome Oscillator, Fractals (fractales), Alligator et Gator.

Ne perdez pas votre temps - analysez l'influence du NFP sur le dollar américain!
Avis de collecte de données
Nous conservons un enregistrement de vos données pour gérer ce site web. En cliquant sur le bouton, vous acceptez notre politique de confidentialité.

Guide pour débutant Forex
Votre guide ultime dans le monde du trading.
Consultez votre boîte de réception !
Dans notre e-mail, vous trouverez notre guide Forex. Appuyez simplement sur le bouton pour l'obtenir !
Avertissement sur les risques : Les ᏟᖴᎠ sont des instruments complexes et ils présentent un risque élevé qui peut vous faire perdre de l'argent rapidement en raison de l'effet de levier.
68,53 % des investisseurs particuliers perdent de l'argent lorsqu'ils tradent des ᏟᖴᎠ avec ce fournisseur.
Vous devez vous demander si vous comprenez le fonctionnement des ᏟᖴᎠ et si vous pouvez vous permettre de prendre des risques élevés qui peuvent mener à d'importantes pertes d'argent.
2022-12-29 • Mis à jour
Les informations données ne sont pas des conseils en investissement
L'économie n'évolue jamais en ligne droite. Les économistes associent étroitement le développement économique à des cycles de hauts et de bas. Les récessions sont considérées comme une partie inévitable d'un cycle économique. On parle de récession lorsque le PIB diminue pendant deux trimestres consécutifs ou plus. De plus, c'est généralement suivi d'une hausse du chômage, d'une baisse des ventes au détail et d'une contraction de l'indice des revenus et de l'indice manufacturier.
Aujourd'hui, presque tous les chefs d'entreprise américains se préparent à une récession, et la plupart des économistes pensent qu'une récession est imminente. La raison en est que la hausse des taux d'intérêt, provoquée par le pic d'inflation, étouffe la croissance en augmentant le coût des cartes de crédit, des hypothèques, des achats de voitures, des prêts commerciaux et de tout emprunt qui alimente une économie. La dernière fois que la Fed a infligé une telle douleur sur un horizon de 12 mois, c'était en 1980, ce qui a entraîné une grave récession économique.
Dans les pays européens, la situation est encore pire, car, en plus des taux élevés, l'économie se débat avec les prix élevés du gaz à l'approche de l'hiver. Comme les entreprises réduisent leurs dépenses en énergie, l'activité économique ralentit.
De 1854 à 1919, la durée moyenne d'une récession a été de 21,6 mois. Toutefois, au fil des ans, les récessions sont devenues plus courtes. Selon les données du National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER), de 1945 à 2009, la récession moyenne aux États-Unis a duré 11 mois. Au cours des 30 dernières années, les États-Unis ont connu quatre récessions. Passons-les en revue.
La dernière récession a débuté en février 2020 et n'a duré que deux mois, ce qui en fait la récession américaine la plus courte de l'histoire.
La bulle du marché de l'immobilier a en partie provoqué la Grande récession. La Grande récession n'a pas été aussi grave que la Grande dépression. Cependant, sa longue durée et ses effets graves lui ont valu un nom similaire. D'une durée de 18 mois, la Grande récession a été presque deux fois plus longue que les récessions américaines récentes.
Au début des années 2000, les États-Unis ont été confrontés à plusieurs problèmes économiques majeurs, notamment l'effondrement de la bulle technologique et les scandales comptables d'entreprises comme Enron, le tout couronné par les attentats terroristes du 11 septembre 2001. L'ensemble de ces problèmes a provoqué une brève récession, dont l'économie s'est rapidement remise.
Au début des années 1990, les États-Unis ont traversé une courte récession de huit mois, en partie causée par la flambée des prix du pétrole pendant la première guerre du Golfe.
Étant donné que les prévisions économiques sont incertaines, il est loin d'être facile de prédire les récessions futures. Par exemple, le COVID-19 était soudainement apparu de nulle part au début de l'année 2020 et, en quelques mois, l'économie américaine s'était effondrée et des millions de travailleurs avaient perdu leur emploi.
La courbe des rendements est un graphique qui représente le rendement d'une série d'obligations du gouvernement américain, depuis les billets d'une durée de quatre mois jusqu'aux obligations à 30 ans. Lorsque l'économie fonctionne normalement, les rendements des obligations à long terme devraient dépasser ceux des obligations à court terme. Par conséquent, les investisseurs craignent une récession lorsque les rendements à long terme sont inférieurs aux rendements à court terme. Ce phénomène est connu sous le nom d'inversion de la courbe des taux, et il a permis de prédire les récessions passées.
Les dépenses de consommation sont le principal moteur de l'économie américaine. Lorsque la confiance des consommateurs décline, c'est-à-dire que les gens n'ont plus envie de dépenser de l'argent, l'économie ralentit. Si les enquêtes révèlent une baisse durable de la confiance des consommateurs, cela pourrait être le signe de difficultés imminentes pour l'économie.
Une baisse importante des marchés boursiers pourrait indiquer une récession puisque les investisseurs vendent les titres pour obtenir des liquidités en prévision d'un ralentissement économique.
Si les gens perdent leur emploi, c'est un mauvais signe pour l'économie. Quelques mois de fortes pertes d'emplois sont le signe d'une récession imminente, même si le NBER ne l'a pas encore déclarée.
Contrairement aux investisseurs, les traders n'ont pas peur des récessions car ils peuvent gagner de l'argent en tradant dans les deux sens, en vendant et en achetant. Cependant, il est essentiel de comprendre le comportement des actifs en période de récession afin de faire le bon choix.
Historiquement, les augmentations du prix du pétrole conduisent à une plus grande inflation future et vice versa. Les dépenses en combustibles énergétiques, qui sont également liées aux prix des transports et de l'alimentation, représentent une part importante du panier de biens de consommation.
En cas de récession, les consommateurs achètent moins, et les producteurs réduisent donc leurs dépenses. La demande d'énergie diminue et le prix du pétrole baisse considérablement. Les traders de pétrole doivent donc garder un œil attentif sur les dépenses de consommation pour prévoir les baisses de prix du pétrole.
Dans le passé, le prix de l'or et les récessions avaient une relation inverse. Lorsque l'économie s'affaiblit, le prix de l'or augmente généralement. Au cours des trois dernières récessions, 2020, 2007 et 2001, le prix de l'or a augmenté alors que la valeur du S&P 500 a diminué.
Cela s'est produit parce que, au cours des deux dernières décennies, les banques centrales ont soutenu les économies par des baisses de taux directeurs et un assouplissement quantitatif (achat de dette extérieure) pendant les récessions, ce qui a entraîné une croissance de l'inflation mondiale.
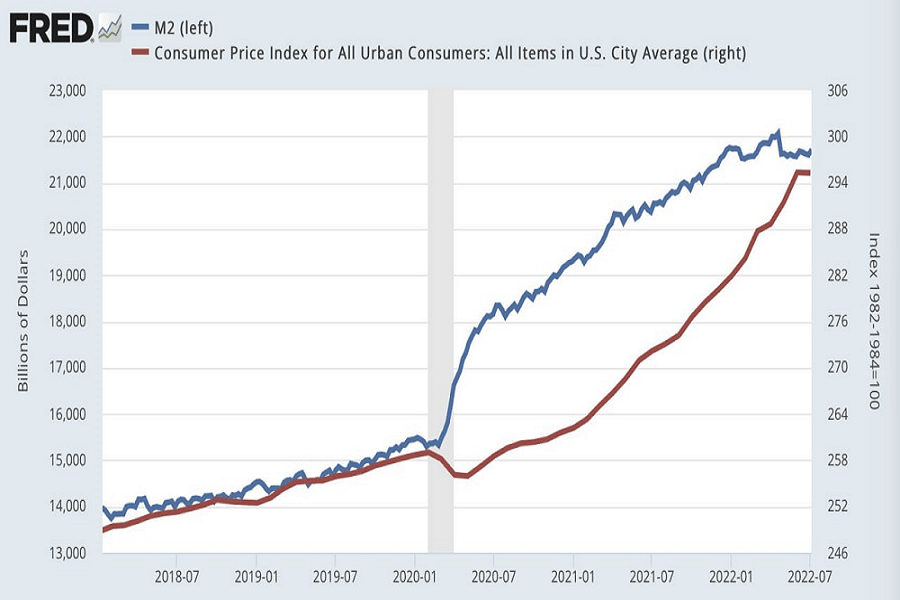
Cette fois-ci ne fera pas exception, notamment à l'approche des élections présidentielles américaines de 2024. Le marché boursier suit généralement l'indicateur de la masse monétaire M2. En d'autres termes, la Réserve fédérale devra imprimer davantage de monnaie pour relancer les actions et l'économie.
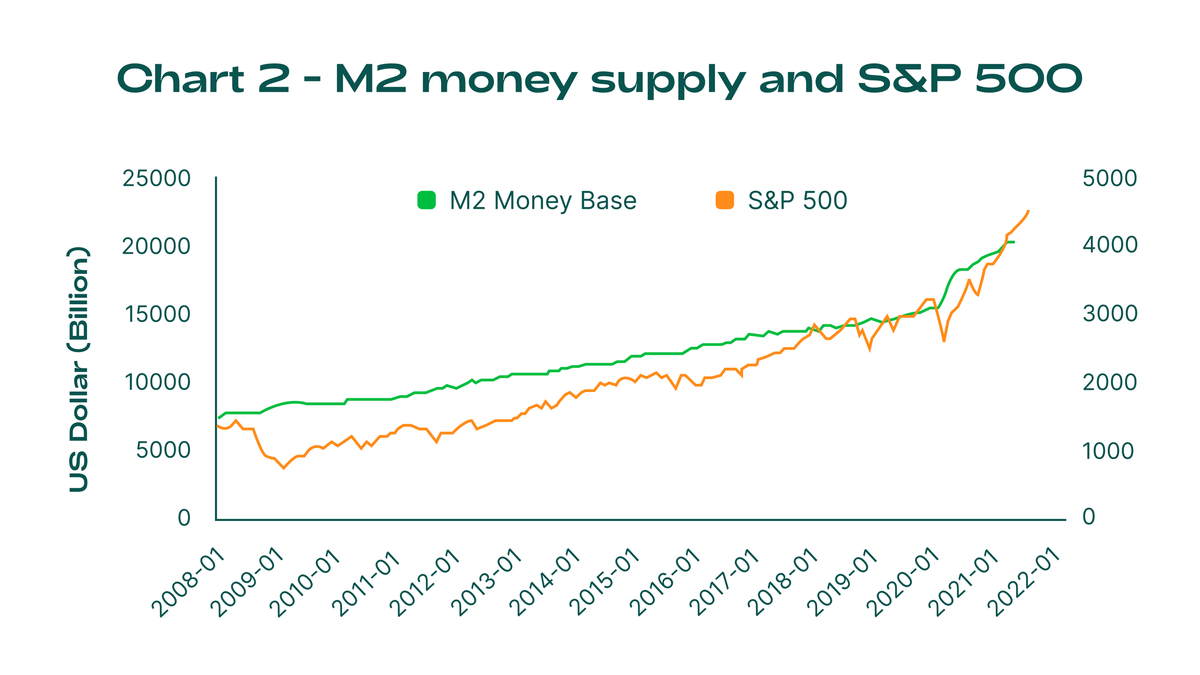
Ainsi, la valeur de l'or augmentera très probablement sur le long terme. Le meilleur moment pour acheter de l'or coïncide avec le début et la fin d'une récession économique, lorsque les banques centrales inversent leurs politiques et commencent à soutenir les économies par de faibles taux d'intérêt et une augmentation de la masse monétaire. À ces moments-là, de grosses sommes d'argent achètent le métal jaune et son prix augmente.
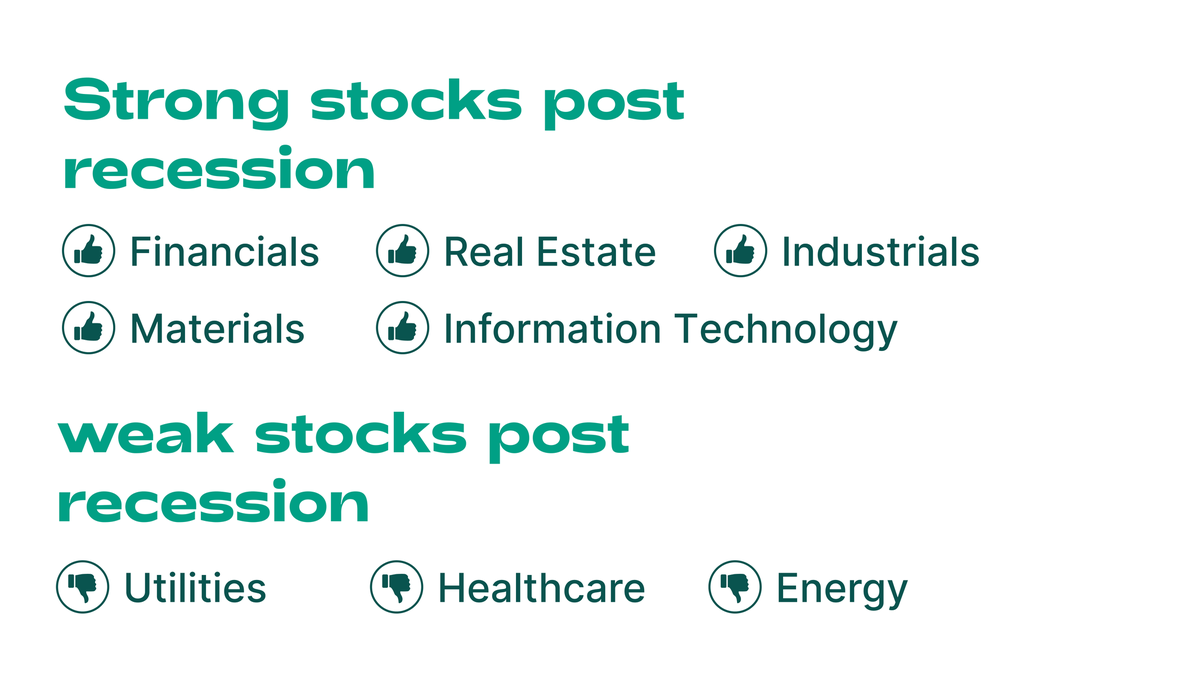
Les récessions ont un impact différent sur les actions, selon le type de société. Certaines sociétés, comme celles du secteur des services publics, des soins de santé et des biens de consommation de base, ont tendance à rester stables pendant une récession. Les sociétés fortement endettées, telles que les sociétés du secteur des voyages et de la technologie, ainsi que les sociétés industrielles, ont tendance à sous-performer sur les marchés.
Le marché des crypto-monnaies est un secteur jeune. Par conséquent, la plupart des projets présentent des dettes élevées. De ce fait, les investisseurs préfèrent se débarrasser de leurs crypto-monnaies lorsqu'une récession commence et à les racheter lorsque l'économie commence à croître.

D'autre part, les secteurs qui sous-performent pendant une récession se comporteront bien lors d'une reprise post-récession. Parmi les exemples, citons les services financiers, l'immobilier, la consommation discrétionnaire, les produits industriels et les matériaux.
Vous pouvez trader avec la volatilité accrue du marché qu'entraînent les récessions en créant un compte de trading et en ouvrant une position avec des CFD. Il s'agit de produits financiers dérivés, qui vous permettent de spéculer sur les marchés en hausse en achetant, ainsi que sur les marchés en baisse en vendant.
Pendant les récessions, l'activité commerciale d'un pays chute et l'économie ralentit. En conséquence, une monnaie est susceptible de chuter parce que le pays devient moins attractif pour les investissements.
Cependant, comme les économies des grands pays sont liées, les récessions ne se produisent pas dans un pays en particulier mais se propagent dans tous les pays. Dans ce cas, les monnaies des pays dont la balance commerciale est la plus stable et qui disposent d'un grand nombre d'actifs en devises (afin que ces pays puissent vendre des actifs étrangers et ramener de l'argent chez eux lorsque la volatilité augmente) sont avantagées par rapport aux autres.
À ce jour, le dollar américain (USD), ainsi que le franc suisse (CHF), sont considérés comme des monnaies refuges.
Si le dollar américain est plus fort par rapport aux devises à rendement plus élevé, cela signifie que les marchés sont probablement mécontents des données ou des nouvelles économiques publiées récemment. Dans ce cas, les investisseurs étrangers achètent des bons du Trésor américain comme valeur refuge. Pour en acheter, ils doivent acheter de l'USD. Lorsque de nombreux investisseurs le font en même temps, ce dollar américain prend de la valeur.
Le franc suisse est une autre monnaie considérée comme une valeur refuge. La stabilité politique, une politique monétaire conservatrice et une économie stable font du CHF une monnaie stable, attirant les investisseurs internationaux en temps de crise.
Malgré les nombreuses crises qui ont secoué les marchés financiers mondiaux, la Suisse a toujours réussi à persévérer sans trop de problèmes.
Si l'économie européenne est confrontée à une récession, le franc suisse (CHF) se renforcera probablement par rapport aux monnaies européennes à rendement plus élevé.
Vendre permet de saisir des opportunités lorsque les marchés sont en baisse. De nombreux traders utilisent des produits financiers dérivés comme les CFD pour vendre un actif. Ces instruments permettent aux traders de prendre des positions spéculatives sur les mouvements de prix d'un actif sans avoir besoin de posséder l'actif lui-même.
Les meilleurs actifs à vendre pendant une récession sont les suivants :
Il peut être risqué d’acheter pendant une récession. C'est pourquoi les traders et les investisseurs attendent le rebond initial lorsque de nombreux actifs atteignent leur minimum. Ils achètent ensuite à ces niveaux, en essayant de tirer le maximum de profit de l'éventuelle reprise post-récession.
Les meilleurs actifs à acheter lors d’une reprise économique sont :
Une récession crée de nombreuses opportunités pour les traders et les investisseurs. En ayant la possibilité de réaliser des trades d'achat et de vente, les traders peuvent augmenter considérablement leur capital en raison de la forte volatilité. Dans le même temps, les investisseurs peuvent acheter les actifs souhaités à bas prix.
Pour réussir, vous devez comprendre la cause de la récession et les moyens possibles pour le gouvernement afin de résoudre le problème (le plus souvent, il s'agit d'une politique monétaire ultra souple). Avec FBS, vous pouvez faire des profits en vendant des actions, des crypto-monnaies et du pétrole pendant une récession. En outre, vous pouvez augmenter votre capital en achetant de l'or et d'autres actifs lorsque l'économie renoue avec la croissance.

Bill Williams est le créateur de certains des indicateurs de marché les plus populaires : Awesome Oscillator, Fractals (fractales), Alligator et Gator.
Les stratégies de tendance sont intéressantes, elles peuvent donner d'excellents résultats sur tous les intervalles de temps et avec tous les types d'actifs. L'idée principale de la stratégie ADX basée sur les tendances est d'essayer d'identifier le début de la tendance.

Les stratégies de contre-tendance sont toujours les plus hasardeuses mais aussi les plus rentables. Nous avons le plaisir de vous présenter une excellente stratégie de contre-tendance qui fonctionne sur tous les marchés et avec tous les actifs.
Votre demande a été acceptée.
Nous vous appellerons lors de l'intervalle de temps que vous aurez choisi
La prochaine demande de rappel pour ce numéro de téléphone sera disponible dans 00:30:00
Si vous avez un problème urgent, veuillez nous contacter via le
Chat en direct
Erreur interne. Veuillez réessayer ultérieurement