Currency Appreciation
Currency Appreciation
What is Currency Appreciation?
Currency appreciation is the strengthening of a currency against other currencies or against gold. If the growth of a monetary unit is less than a few percent, it is considered a market fluctuation, but if it is more, it is regarded as a currency appreciation.
In the Forex market traders trade currency pairs in order to make a profit due to the increase in the rate of the base currency against the counter currency. To quickly calculate the value of a particular currency, use the currency converter.
How Currency Appreciation happens?
Most often, currency appreciation occurs when it is necessary to reduce the rate of inflation. This can be done artificially, that is, through currency intervention. If in the past the central bank or the government had to increase the volume of gold reserves, today it is carried out by buying foreign currency in exchange for domestic currency. Thus, the exchange rate of the national currency increases.
Natural currency appreciation happens when the market sentiment changes, and the demand for the national currency of the country grows.
Currency Appreciation and stocks
A stock is a security that confirms a shareholder's right to hold a stake in a company. Even if you own a minimal part of the company, you are entitled to receive dividends and also can earn from the increase in the value of the shares if you decide to sell them.
The value of the stock depends primarily on the success of the company, the economic sector, and, of course, the global economy. The state of the company's business and, consequently, the stock price, among other things, is affected by the exchange rate of the national currency and inflation. The higher the inflation rate, the lower will be the real return on the stock, and vice versa. Depending on the rise or fall of the currency, you can predict how this will affect the solvency of the company and the value of its shares.
Furthermore, one should pay attention to whether the issuer is an exporter or importer. Revaluation is beneficial primarily for companies that are engaged in imports, because the prices of foreign goods go down.
Main economic effects of Currency Appreciation
The consequences of currency appreciation can be summarized as follows:
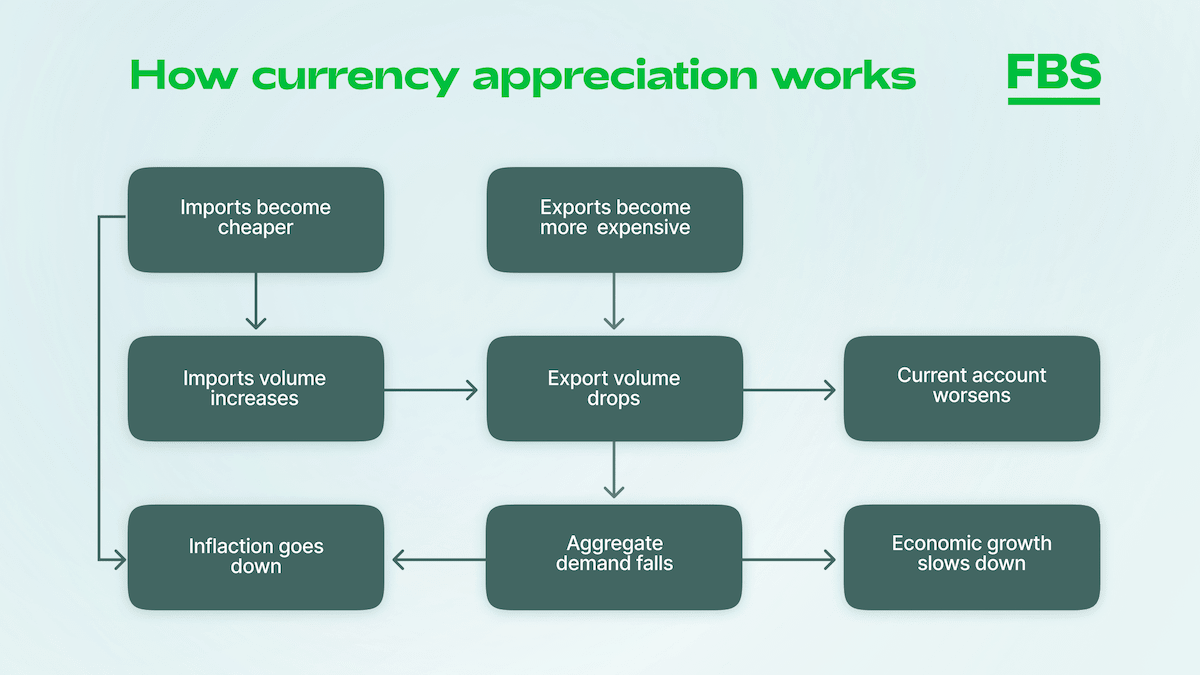
- Growth of export costs. Exports decline because selling goods abroad brings the country less money. Consequently, domestic production drops because it becomes less profitable to produce and sell local goods abroad than to import foreign goods. In turn, the depreciation of the local currency leads to a decrease in the purchasing capacity of foreign investment, and so there is a capital outflow.
- Cheaper imports. With the appreciation of the domestic currency, it becomes more profitable to obtain foreign goods and assets, as they can be purchased at a lower price than local. Thus, the inflation rate is reduced due to the influx of cheap exported goods.
Here is a diagram to illustrate the point:
Factors that cause Currency Appreciation
Financial analysts identify two reasons for the currency appreciation:
- Inflation and interest rates. As we mentioned earlier, the main reason for currency appreciation is high inflation as well as low real interest rates. The national currency is depreciating, and this leads to lower real rates and higher commodity prices. In this circumstance the domestic currency needs to be stabilized.
- Investor sentiment. This is the second, but no less important reason, which derives from the percentage of inflation. In the case of high inflation, it is not profitable to invest in shares of local companies, because the dividends will be meager. And if the inflation rate exceeds the interest rate, they will be even worse — negative.
Investors and traders alike can monitor global financial markets for the highest currencies and pay attention to signals and events that may cause a currency to appreciate.
Examples of Currency Appreciation
As an example of natural currency appreciation, we can consider the rise of the Swiss franc (CHF) in 2015. The Swiss National Bank abandoned its previous financial policy and stopped controlling the CHF exchange rate. This led to a sharp rise in the Swiss national currency by 40% (38% against the USD and 41% against the EUR to be exact) and the major repercussions for the global economy.
And the artificial currency appreciation, which is carried out deliberately in order to lower inflation, took place, for example, in China in 2005. The government abandoned the fixed CNY/USD exchange rate in favor of a peg to a basket of currencies as part of the new financial policy. That way they raised the value of the CNY by 2% first, and by 2010 by more than 20%.
Conclusion
Currency revaluation is not a simple process that does not happen without the influence of the state and the central bank on the economic policy. It has both positive and negative effects, for financial markets, traders, investors, and ordinary people alike. That is why it is important to follow the exchange rates and economic events, always be up to speed and secure your wallet in time.
2022-12-20 • Updated