Divergence
Divergence
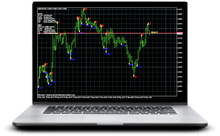
Divergence in the Forex environment generally refers to a discrepancy in the direction between the price and the indicator. Normally, an oscillator like RSI is measured against the chart.
There are two types of divergence: a regular and a hidden one. Each may be either bullish or bearish.
Regular bullish divergence.
It occurs in a downtrend; the price forms a lower low and the indicator forms a higher low. If you draw a line through each pair of lows for the price and the indicator, the two lines will appear being pinched together towards the end. This may be a signal of a market reversal in the upward direction.
Regular bearish divergence.
It occurs in an uptrend; the price forms a higher high and the indicator forms a lower high. The two lines fall apart towards the end. This may be a signal of a downward market reversal.
Hidden bullish divergence.
It occurs in an uptrend; the price forms a higher low and the indicator forms a lower low. The two lines fall apart towards the end. This would signal the market’s intention to rise later on.
Hidden bearish divergence.
It occurs in a downtrend; the price forms a lower high and the indicator forms a higher high. The two lines get pinched together towards the end. This would mean that the market is preparing to drop further.
2020-04-24 • Updated